New to CDISC
After learning clinical data, the next logical step is to learn CDISC, Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium. Both pharma and medical device SAS programmers can benefit from this page. See also New to Clinical Data, CDISC Programming, CDISC 101 Mapping Training videos, Statistical Analysis and New to SAS® Programming. See Introduction to CDISC on SAS Savvy webinar and Pinnacle 21 Demo webinar. Common Data Models for clinical data.
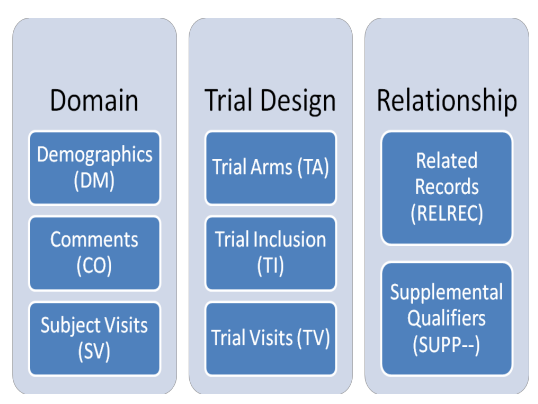
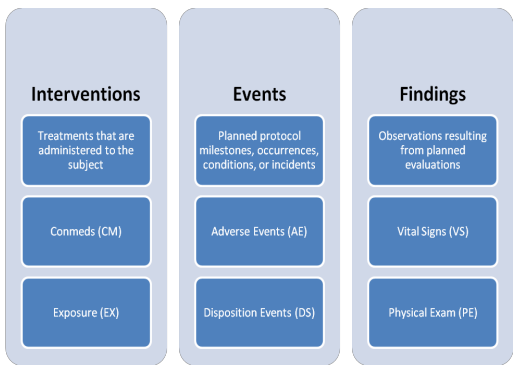
SDTM OnLine Specification Control Terminology (Online)

- Welcome to CDISC
- CDISC Glossary
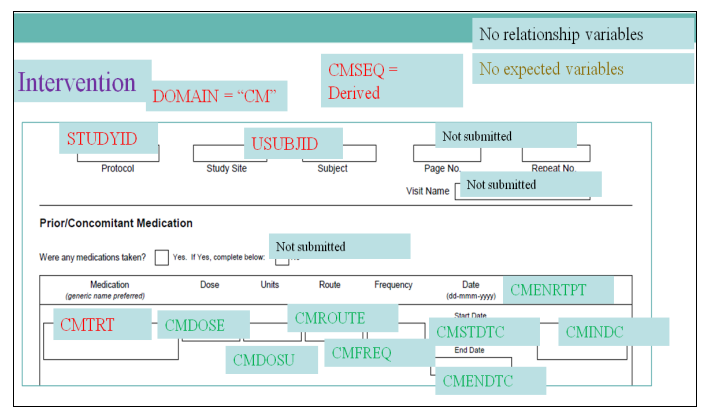
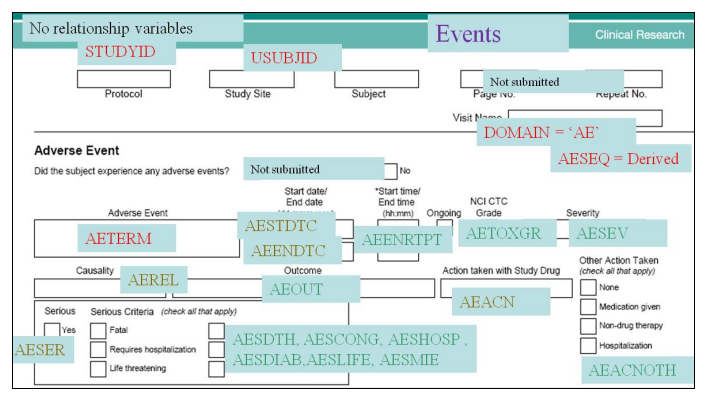
- Annotated Case Report Forms
- Introduction to CDISC
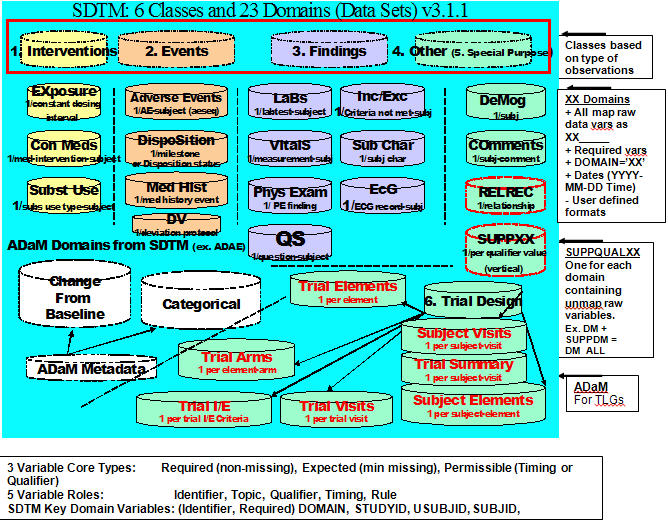
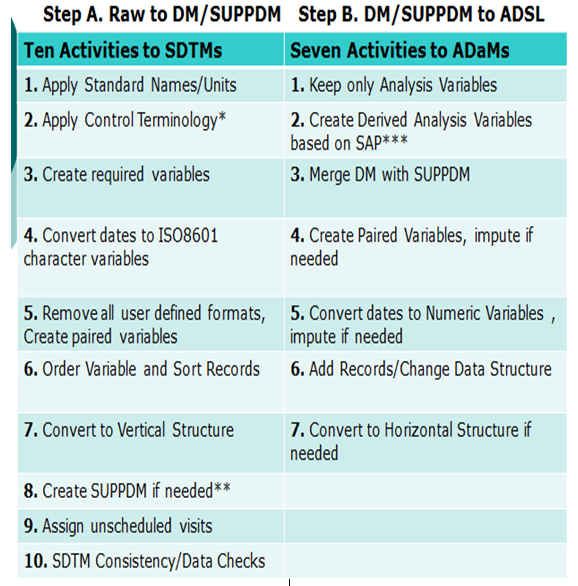
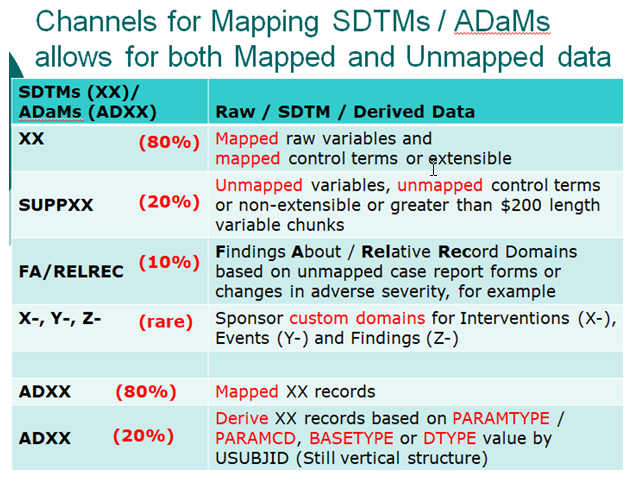
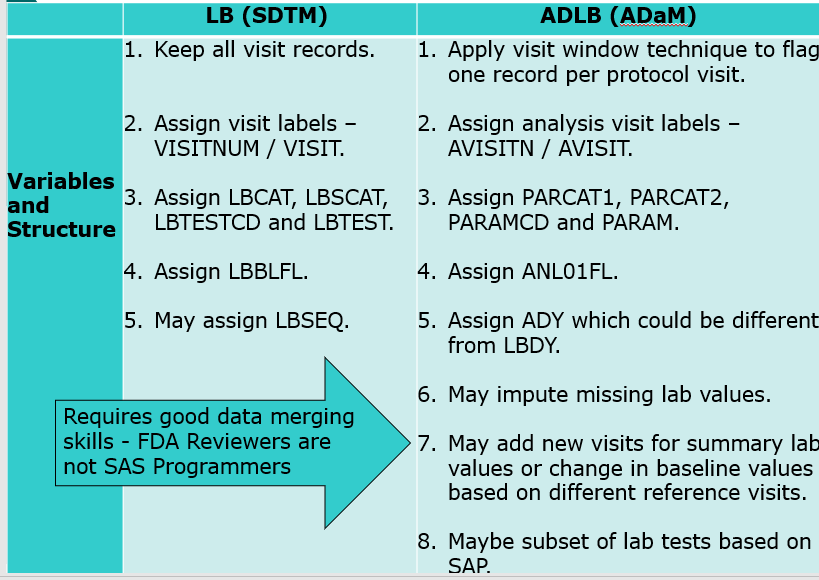
- Compare SDTMs
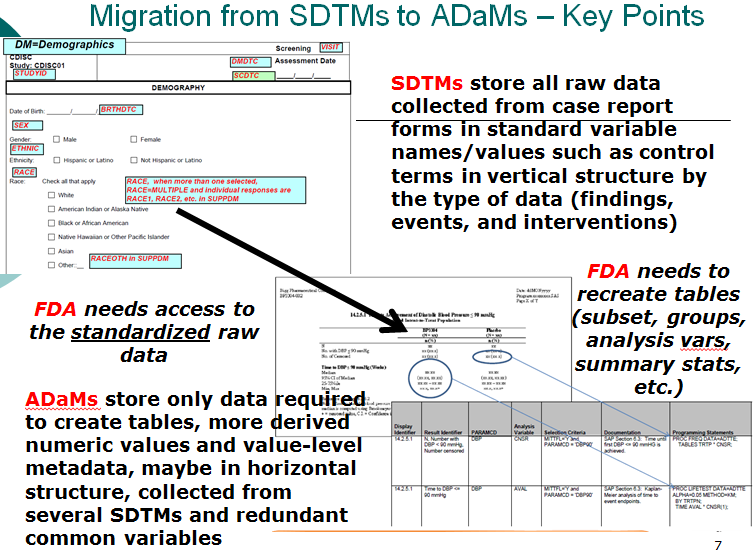
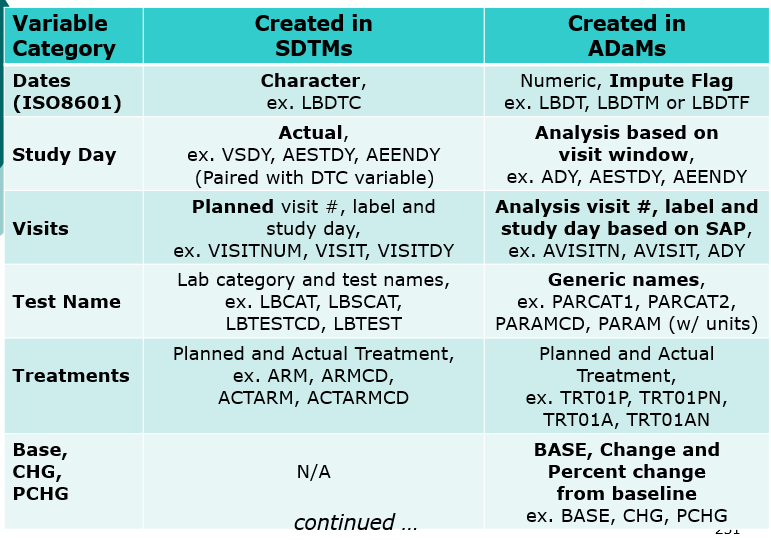
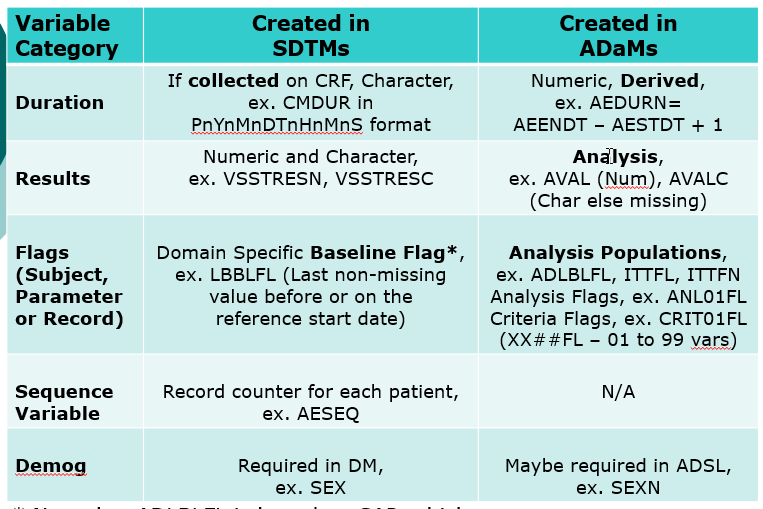
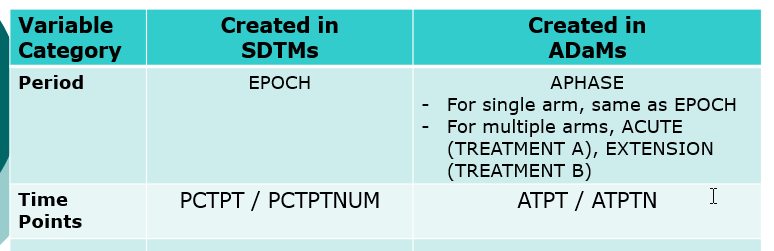
- Compare SDTMs and ADaMs
- Clinical Programmer Duties
- CDISC White Papers
- General SAS Papers
CDISC Primer (Introduction Videos on SEND, CDASH, SDTMIG, ADaMs)
CDISC Glossary (CDISC Blog) (Top)
Annotated Case Report Form (CRF) (Top)
Introduction to CDISC (Blog) (Top)
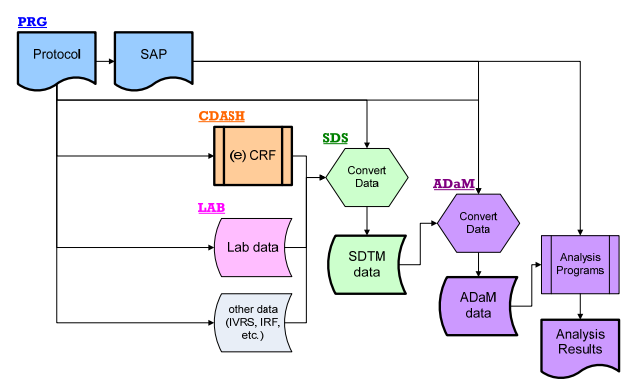
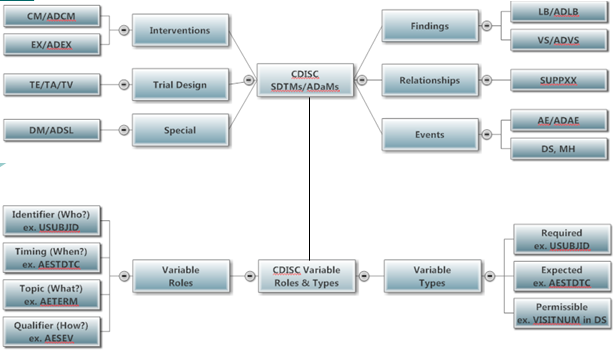
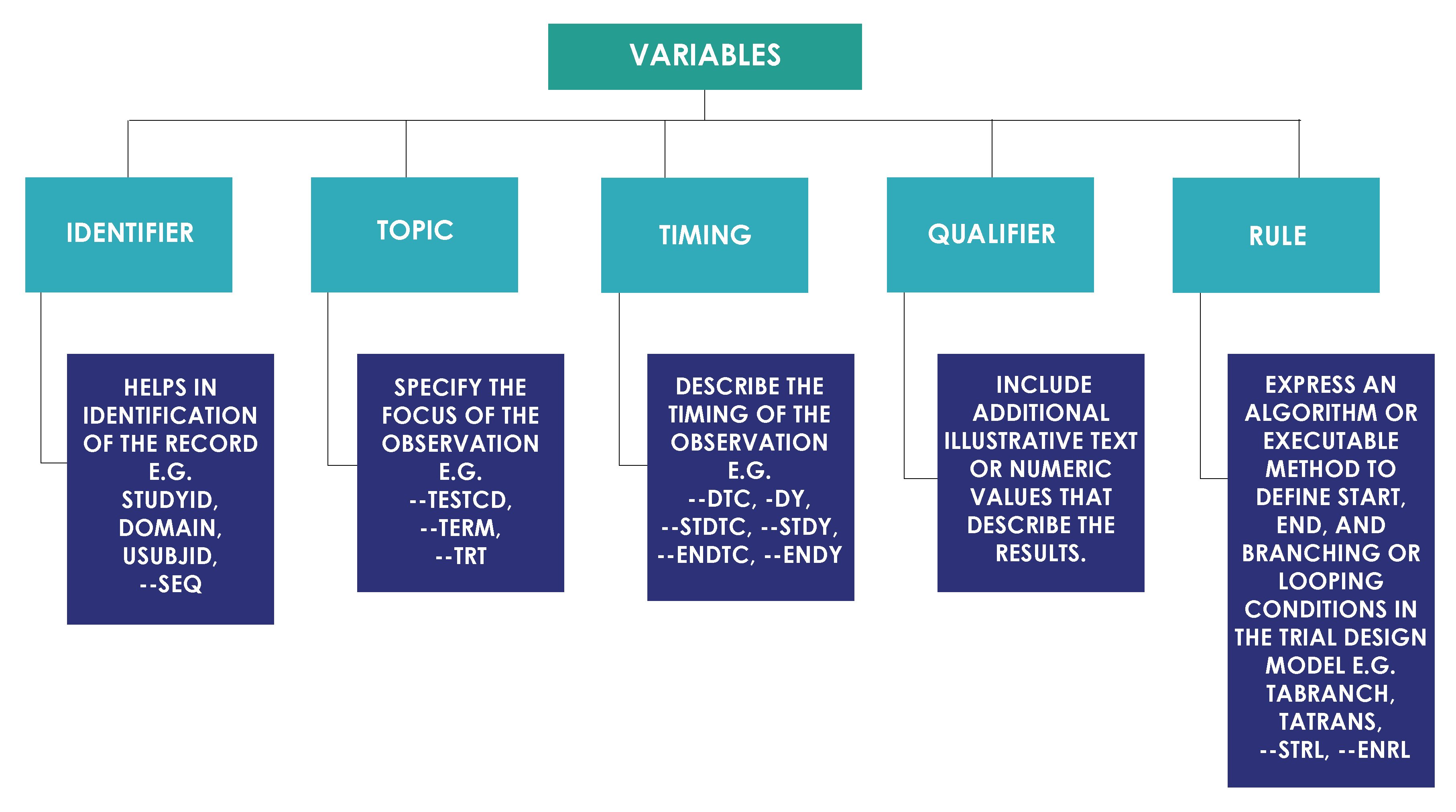
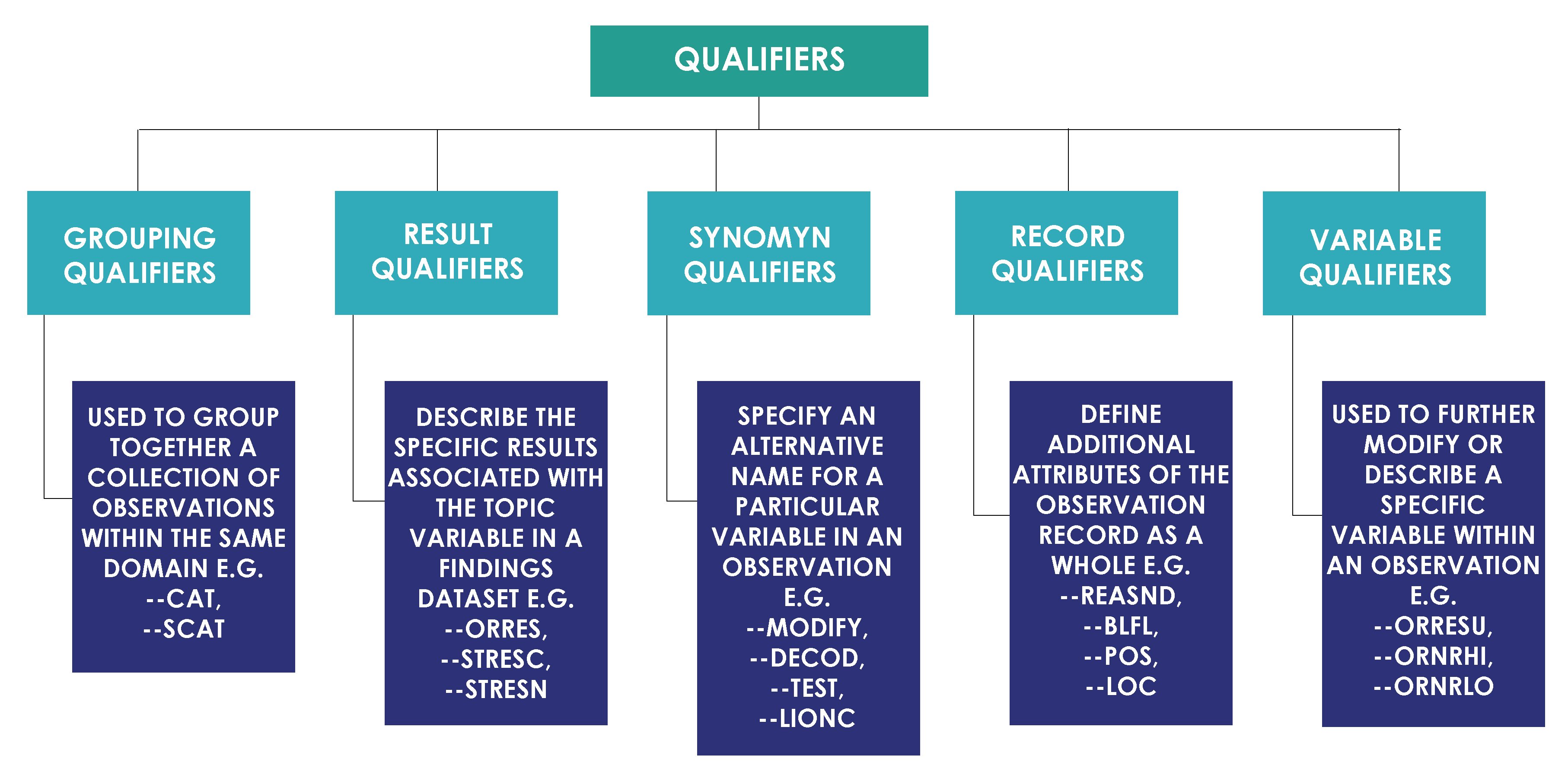
- MindMap: Clinical Process Flow, CDISC, Control Terminology
- Specifications: SDTMs, ADaMs
- Timeline: Start study, End study, SDTMs/ADaMs, Database lock and TLGs
- SAP: Statistical Analysis Plan, Template
- CRF: Case Report Forms, Randomized Controlled Trial
-
TLGs Table Shells: Tables, Lists and Graphs, QC Checklist
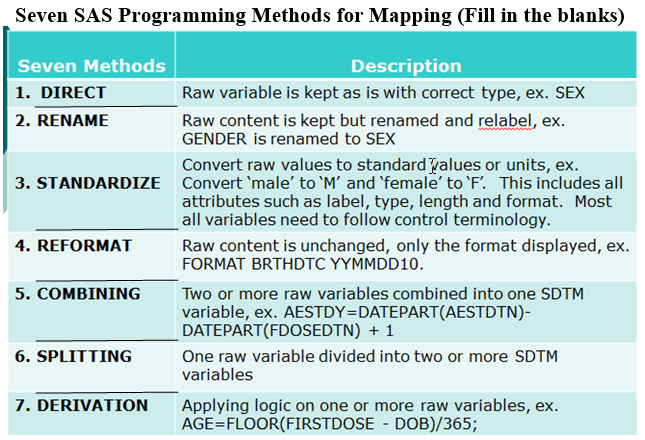
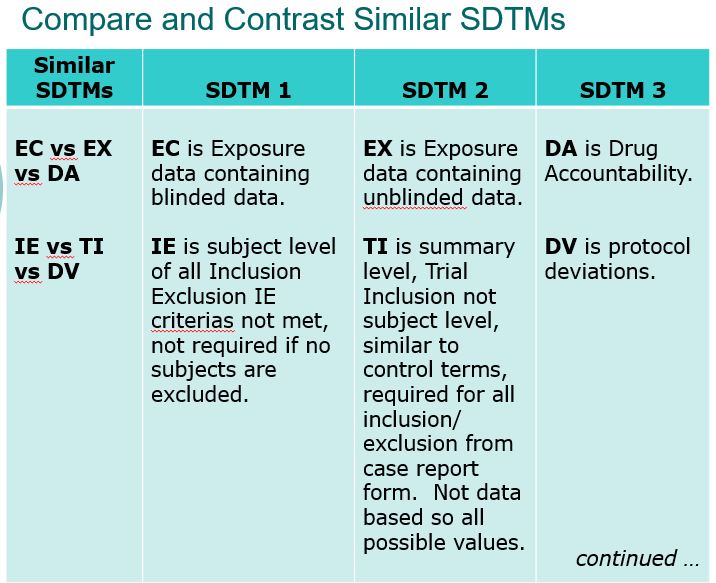
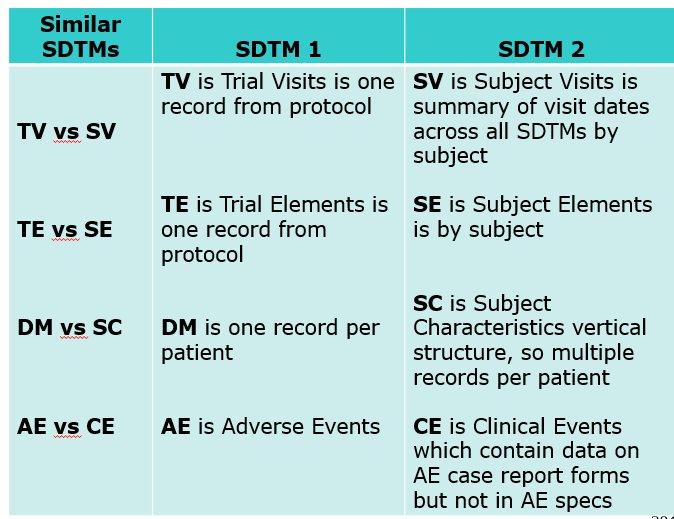
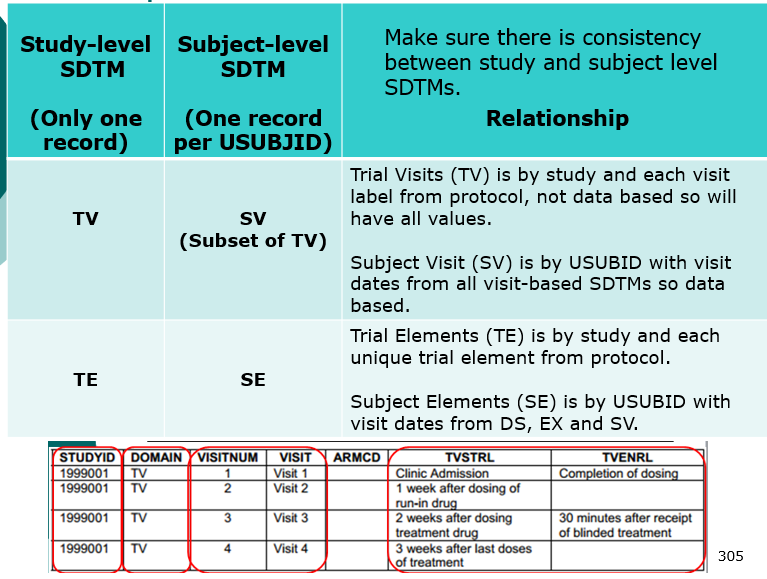
Clinical Programmer Duties (Top)
Responsible for building programs to create SAS datasets from the clinical database, external data sources, and other sources while following the clinical study's protocol or statistical plans.
- Primary responsibilities
- Build SAS datasets from clinical database.
- Develop SAS macros, templates and utilities for data cleaning and reporting.
- Utilize SDTM guidelines to build datasets.
- Communicate with an internal team to create deliverables for pharmaceutical and biotechnology clients.
- Implement analyses specified in the protocol or the Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) while working with the project statistician.
- Ensure CRF meets the guidelines of the protocol and check for consistency and adequacy.
- Write SAS programs to generate tables, listings, and figures and analysis datasets.
- Review CRF annotations and data specifications.
- Work in tandem with Biostatistics and Data Management member on various clinical projects.
- Identify and edit checks per the data validation plan or data management plan.
- Study management reports using SAS.
- Validate the programmed analysis datasets, tables, listing and figures.
- Perform analyses defined in the statistical analysis.
- Prepare clinical and statistical summary reports.
- Communicate with programming and statistics leads.
- Utilize SAS programming skills within protocol team and perform all programming required for clinical trial analysis and reporting.
- Perform quality control on final reports.
- Develop SAS coding and table templates for preparing, processing and analyzing clinical data.
- Establish monitoring of data transfers for ongoing trials to identify study conduct or data quality issues.
CDISC White Papers (Top)
1. Practical Methods for Creating CDISC SDTM Domain Data Sets from Existing Data, Robert Graebner [Tutorial, Comments]
2. Introduction - Introduction to the CDISC Standards, Sandra Minjoe
3. CDISC: Why SAS® Programmers Need to Know, Victor Sun4. A Relational Understanding of SDTM Tables, John R. Gerlach, Glenn O’Brien [HOW]
5. SDTM What? ADaM Who? A Programmer’s Introduction to CDISC, Venita DePuy [Basic, Technical Screening, Inclusion/Exclusion]
6. An Introduction to SDTM ± 298 pages in 20 minutes?!, Jennie Guirk [Part 1 Presentation, Part 2 Presentation]
7. Backpacking Your Way Through CDISC: A Budget-Minded Guide to Basic Concepts and Implementation, Rachel Brown, Jennifer Fulton [Definitions]
8. Tips for efficient CDISC eCRT production, Lanting Li, Yu Zhu, Huan Zhu [Unscheduled, Not Submitted, Checklist, Process, Define.xml]
9. SDTM to ADaM + Standard TLF Reporting Code = Efficient A&R: A Middle-to-End Approach, Valerie Williams [Presentation]
General SAS Papers (Top)
1. Clinical Trials Terminology for SAS Programmers, Sy Truong
2. SAS® PROGRAMMER TO CLINICAL SAS PROGRAMMER, Gayatri Karkera, Neha Mohan [Phase I, II, III, IV, Endpoints]
3. Success As a Pharmaceutical Statistical Programmer, Sandra Minjoe, Mario Widel
4. THE ROLE OF SAS PROGRAMMERS IN CLINICAL TRIAL DATA ANALYSIS, Ming Wang
5. SAS® Programming for the Pharmaceutical Industry, Brian C. Shilling, Carol Matthews [QC]
6. The 5 Most Important Clinical SAS Programming Validation Steps, Brian Shilling
8. Intro to Longitudinal Data: A Grad Student “How-To” Paper, Elisa Priest,Ashley Collinsworth
9. Longitudinal Data Techniques: Looking Across Observations, Ronald Cody
10. Pharma Company Questions and Answers, J.J. Hantsch
11. Careers in Biostatistics and Clinical SAS® Programming An Overview for the Uninitiated, Justina Flavin [Roles, Responsibilities]
12. Statistical Programming for Dummies [Presentation, Investigator’s Brochure (IB)]
14. Managing the Evolution of SAS® Programming, Carey Smoak
15. Empowering SAS® Programmers: The Role of the Manager, Carey Smoak
16. Skills for SAS® programmers in Epidemiology, Philip Holland [Presentation]
17. A Short Introduction to Longitudinal and Repeated Measures Data Analyses, Leanne Goldstein
18. The Baker's Dozen: What Every Biostatistician Needs to Know, AnnMaria De Mars [INCIDENCE, SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY, RELATIVE RISK, RISK DIFFERENCE AND ODDS RATIO, FISHER’S EXACT TEST, MCNEMAR]
19. Expediting Access to Critical Pathology Data, Leanne Goldstein, Rebecca Ottesen, Julie Kilburn, Joyce Niland [Metastasis]
20. GCP101, Good Clinical Practices OR “Why we do What we do the Way we do it“, Elaine Dempsey
21. CLINICAL PROGRAMMING FOR NOVICE, Ramesh Ayyappath [Investigator’s Brochure (IB)]
22. Making of a Stat Programming Project Manager, Manjusha Gode, Ajay Sathe [Presentation] [Work-Life balance: Making it a reality]
23. Industry Standard Good Programming Practice for Clinical Trials (Using SAS), Mark Foxwell
24. Good Programming Practices at Every Level, Maria Dalton [Programming Style, TA]
25. The Anatomy of Clinical Trials Data: A Beginner’s Guide, Venky Chakravarthy [Glossary]
26. Stretching Data Training Methods: A Case Study in Expanding SDTM Skills, Richard Addy
27. The Super Genius Guide to Generating Dummy Data, Brian Varney
28. Producing a Format Library and Test Data for Case Report Forms using a Data Define Table
30. THE ROLE OF SAS PROGRAMMERS IN CLINICAL TRIAL DATA ANALYSIS, Ming Wang
31. Successfully On-Boarding SAS® Analysts, Aaron Augustine
32. Starting a New SAS Project with Effectiveness and Success, Flora Liu
33. ONBOARDING A JUNIOR STATISTICAL PROGRAMMER IN 10 WEEKS MY STORY FROM UNIVERSITY TO FIRST ANALYSIS DELIVERY, Pieter Coppens [Presentation]
34. How to review a CRF - A statistical programmer perspective, Elsa Lozachmeur
35. Validating Your SAS Systems, Sy Truong [Installation, Operational, Performance Qualifications]
37. Good Programming Practice [GPP] in SAS® & Clinical Trials, Srinivas Vanam, Manvitha Yennam, Phaneendhar Vanam [Programming Style]
38. Training Statistical Programmers on SAP Review Skills, Sascha Ahrweiler [Statisticians]
39. A Programmer’s Guide to Statistical Procedures, Jim Edgington
40. Statistics for Clinical Trial SAS Programmers 1: paired t-test, Kevin Lee
41. Statistics: The Fourth Dimension of a “Statistical Programmer”, Gauri Khatu, Vibhavari Inamda
42. Oncology Trials 101 - The Basics and Then Some, Dave Polus
43. Clinical Trial Reporting Using SAS/GRAPH® SG Procedures, Susan Schwartz
44. Practice Makes Perfect: Training and Performing in the Pharmaceutical Industry, Sunil Gupta